Prepared by: Yomna Al-Zubairy
In recent years, Yemen has witnessed numerous political, economic, and humanitarian crises. These crises have worsened with the outbreak of conflict in Yemen, leading to the destruction of infrastructure, deterioration of basic services, and rising unemployment and poverty rates, prompting many to emigrate in search of security, stability, and better life opportunities. A significant portion of these emigrants are women seeking better job prospects and more stable lives.
The emigration of Yemeni women has exacerbated the shortage of qualified personnel in various sectors of Yemen, such as healthcare and education, significantly impacting the country’s development. However, Yemeni women emigrants face considerable challenges in host countries, including discrimination, racism, difficulty finding jobs, vulnerability to exploitation, difficulties adapting, and homesickness.
Following these events, the Information and Opinion Polling Unit at Yemen Information Center conducted an opinion poll on “Leading Women’s Voices in the Yemeni Diaspora” to examine the views of a sample of Yemeni society regarding Yemeni women abroad, their impact on the country’s development, and the main difficulties they face abroad.
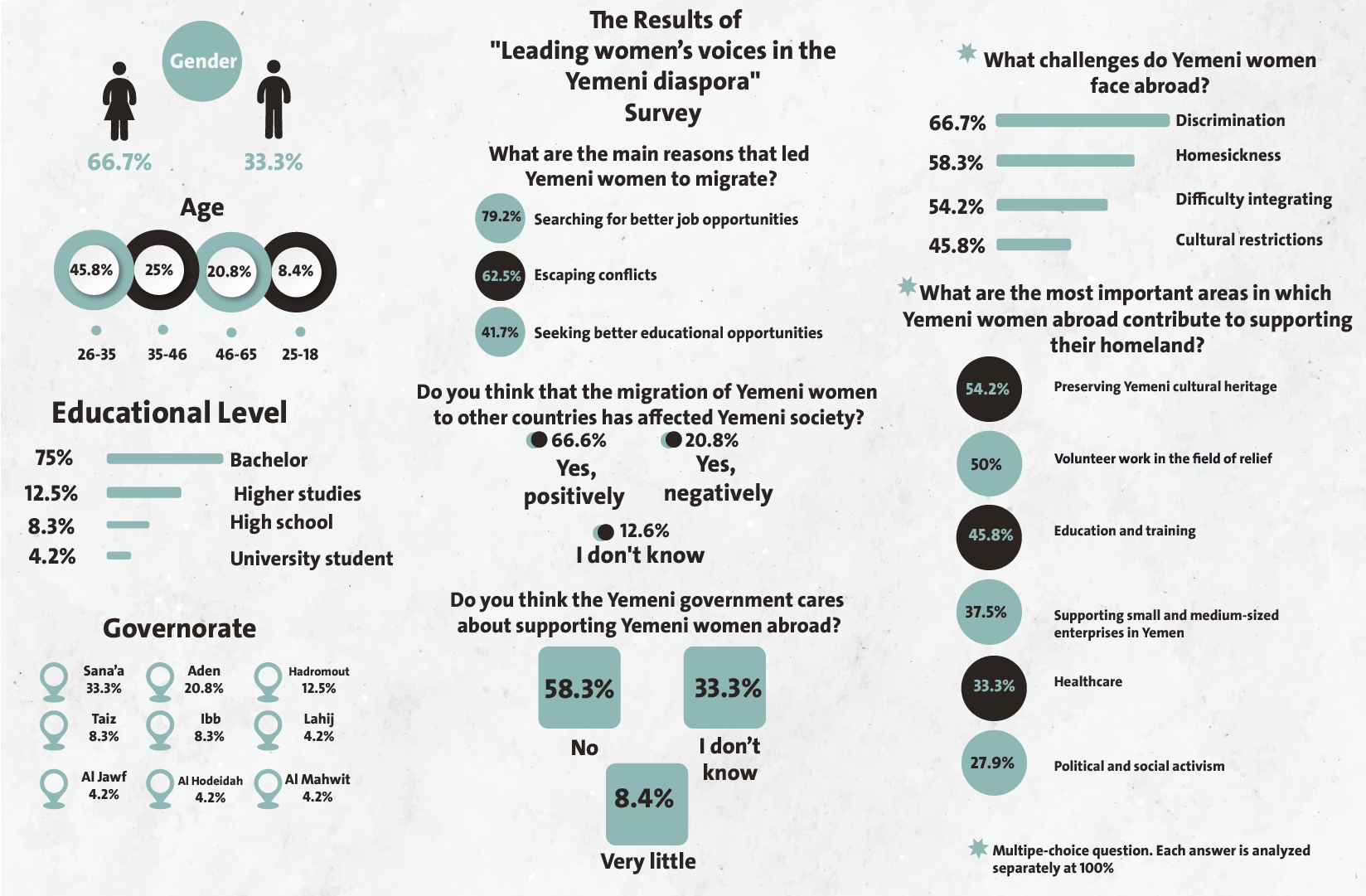
The poll surveyed a sample of 124 participants from various parts of Yemen. The gender distribution among participants was almost equal, with 66.7% female and 33.3% male. Participants were distributed across different age groups; the 26-35 age group constituted the largest percentage (45.8%), followed by the 36-45 age group (25%). The poll also included 20.8% of those aged 46-65 and 8.4% from the 18-25 age group.
Regarding education, those with bachelor’s degrees were the most represented group (75%), followed by those with higher degrees (12.5%). 8.3% held high school diplomas, and 4.2% were university students.
It included 9 Yemeni governorates; Sana’a governorate had the highest percentage of participants (33.3%), followed by Aden (20.8%), Hadhramaut (12.5%), Taiz (8.3%), and Ibb (8.3%). 4.2% of participants were from Lahj, Al-Jawf, Al Mahwit and Al-Hudaida governorates.
Key Findings
Initially, we asked participants about the main reasons driving Yemeni women to emigrate. Their responses were as follows*:
- Seeking better and more stable job opportunities (79.2%).
- Escaping conflicts and political unrest (62.5%).
- Seeking better educational opportunities (41.7%).
Regarding the impact of Yemeni women’s emigration to other countries on Yemeni society, 66.6% stated that it had a positive impact, 20.8% said it had a negative impact, and 12.6% said they had no opinion.
Concerning the support provided by the Yemeni government to Yemeni women abroad, 58.3% said the government provides no support, 33.3% said they had no opinion, and only 8.4% said the government provides minimal support.
Regarding the areas in which Yemeni women abroad contribute to supporting their homeland, the participants’ responses were as follows*:
- Preserving Yemeni cultural heritage (54.2%).
- Volunteer work in relief (50%).
- Education and training (45.8%).
- Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises in Yemen (37.5%).
- Healthcare (33.3%).
- Political and social activity (27.9%).
Regarding the challenges faced by Yemeni women abroad, participants identified the following*:
- Discrimination and racism (66.7%).
- Homesickness (58.3%).
- Difficulty integrating into the new society (54.2%).
- Cultural constraints (45.8%).
In conclusion, the results of this survey reveal the depth of the crisis facing Yemeni women, both at home and abroad. While emigration may be a refuge for many seeking a better life, it also presents new burdens and significant challenges. Despite the challenges, Yemeni women abroad have demonstrated resilience and creativity, contributing to preserving Yemeni cultural heritage and supporting their country.